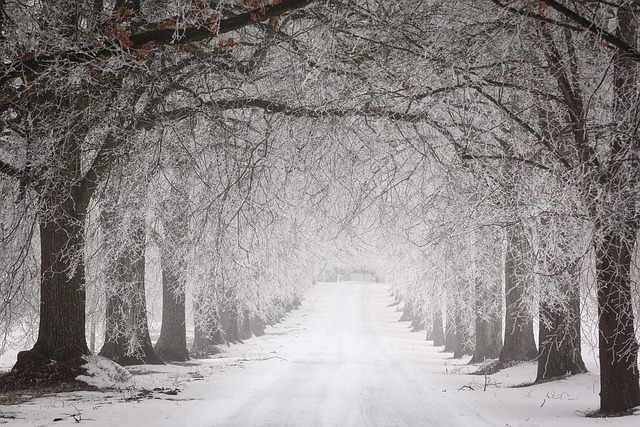
In cold-weather regions, cold weather plumbing faces unique challenges from fluctuating temperatures, heavy rainfall impact, and humidity effects. These factors accelerate pipe corrosion and contribute to frost heave, potentially damaging or bursting pipes. To combat these issues, seasonal maintenance is crucial. Regular inspections, proper insulation, using corrosion-resistant materials, efficient drainage systems, cleaning, and leak checks are essential strategies that ensure pipe stability and prevent structural failures throughout the year.
“In regions subject to extreme cold and variable weather conditions, frost heave poses a significant threat to underground pipes. This natural phenomenon, caused by rapid freezing and thawing cycles, can lead to pipe instability and potential damage. Understanding the mechanisms behind frost heave is crucial for addressing its impact on plumbing systems. This article explores the role of heavy rainfall and temperature fluctuations, seasonal humidity effects, and essential strategies to mitigate pipe corrosion, offering insights into maintaining stability throughout the year.”
- Understanding Frost Heave: A Common Cold Weather Plumbing Issue
- The Role of Heavy Rainfall and Temperature Fluctuations in Pipe Instability
- Humidity Effects on Underground Pipes: A Seasonal Maintenance Concern
- Mitigating Pipe Corrosion: Essential Strategies for Year-Round Stability
Understanding Frost Heave: A Common Cold Weather Plumbing Issue

Frost heave is a common yet often overlooked issue in cold weather plumbing, particularly affecting underground pipes. This phenomenon occurs when water within pipes freezes and expands, putting immense pressure on the surrounding pipe material. The resulting upward thrust can cause pipes to heave out of the ground, leading to leaks, damage, or even burst pipes. Understanding this process is crucial, especially given the frequent temperature fluctuations and heavy rainfall impact during colder months.
In regions with high humidity levels, the problem is exacerbated as moisture in the soil contributes to faster ice formation inside pipes. To mitigate these effects, seasonal maintenance is essential. Regular inspections and proper insulation can prevent pipe corrosion and reduce the risk of frost heave damage. By addressing these issues proactively, homeowners and plumbing professionals alike can ensure the stability and longevity of underground piping systems during cold weather.
The Role of Heavy Rainfall and Temperature Fluctuations in Pipe Instability

In regions with cold weather plumbing issues, heavy rainfall and temperature fluctuations play a significant role in the instability of underground pipes. During colder months, water within pipes can freeze, causing them to expand and exert pressure on their surroundings. This process, known as frost heave, leads to potential pipe damage or even breakage, particularly if the ground above is not sufficiently stable. Heavy rainfall, while beneficial for overall hydration, can exacerbate these issues by introducing excess water that may seep into frozen pipes, further contributing to corrosion and structural compromise.
Temperature fluctuations also contribute to pipe instability through a process called thermal expansion and contraction. As temperatures rise and fall, pipes heat up or cool down at different rates than the surrounding soil, leading to warping or misalignment. This movement can cause stress points in joints and fittings, increasing the risk of leaks or structural failures. Maintaining pipes during seasonal changes, including regular checks for corrosion and signs of damage, is crucial to prevent these issues. Additionally, proper drainage systems that manage humidity effects are essential to mitigate potential long-term damage caused by both heavy rainfall impact and temperature fluctuations on underground piping infrastructure.
Humidity Effects on Underground Pipes: A Seasonal Maintenance Concern

In cold weather regions, underground pipes are subjected to significant seasonal changes, with ?cold weather plumbing being a critical concern for homeowners and maintenance teams alike. One often overlooked factor contributing to pipe instability is humidity—a byproduct of heavy rainfall and temperature fluctuations. As water seeps into the ground, it interacts with the pipe’s material, leading to potential corrosion over time. This process can weaken the structure of pipes, making them more susceptible to damage during frost heave events.
The impact of humidity becomes more pronounced when combined with cold temperatures. The freezing and thawing cycles further exacerbate pipe corrosion, as water expands within the pipes, causing stress at joints and connections. To mitigate these seasonal maintenance issues, regular inspection and treatment are essential. Preventative measures such as sealing vulnerable areas and applying protective coatings can help extend the lifespan of underground pipes, ensuring they remain stable and functional throughout varying weather conditions.
Mitigating Pipe Corrosion: Essential Strategies for Year-Round Stability

To mitigate pipe corrosion, especially in regions experiencing cold weather and heavy rainfall, a proactive approach is essential. Seasonal maintenance plays a pivotal role in ensuring underground pipes remain stable year-round. During colder months, temperature fluctuations can lead to frost heave, causing pipes to expand and contract. This mechanical stress can accelerate corrosion, particularly when coupled with high humidity levels. Therefore, regular inspections are crucial to identify any signs of damage or weakness.
Implementing specific strategies like using corrosion-resistant materials, insulating pipes to prevent extreme temperature changes, and installing protective coatings can significantly extend their lifespan. Additionally, proper drainage systems should be in place to redirect excess water away from pipe structures, reducing the impact of heavy rainfall. Seasonal maintenance routines that include cleaning, flushing, and checking for leaks are also vital to maintaining optimal pipe stability.